

Since meiosis consists of first and second meiotic divisions, these phases occur twice, each designated as I and II. Both mitosis and meiosis are comprised of these chronological phases: (1) prophase, (2) metaphase, (3) anaphase, and (4) telophase. Meiosis produces four cells that are genetically dissimilar and in which the chromosomes are reduced by half. Mitosis produces two cells that are genetically identical. Cell divisions in eukaryotes, particularly mitosis and meiosis, are important since they give rise to new cells. mitosis and meiosis) and is highlighted by the alignment of condensed chromosomes at the metaphase plate. Metaphase is the phase following prophase and preceding anaphase of cell divisions (i.e. Image Credit (from left to right): Shoba Shanti, Edmund Wilson, and Plant and Soil Sciences. From left, metaphase under a microscope (onion root tip), metaphase in animal cell diagram, and another metaphase diagram with labeled parts. The image below is the metaphase microscope and diagram. If it takes place at the mitosis chromosome, this can result in cells becoming cancer. In the case of meiosis, it can result in birth abnormalities and offspring that are unable to survive. This can result in either an excessive number of chromosomes or an inadequate number of chromosomes in the daughter cells that are produced. If this is indeed the case, then the chromosomes will be sorted into incorrect cells. This might cause errors in the cell’s ability to reproduce. If these checkpoints are missed or do not function properly, the cell will enter anaphase before the chromosomes are correctly connected to microtubules and positioned on the metaphase plate. The spindle assembly checkpoint is comprised of a complex network of systems that work together to verify that chromosomes are correctly divided.īoth mitosis and meiosis go through a spindle assembly checkpoint during metaphase, although the chromosomes align in distinct ways during these two processes. The checkpoint for the assembly of the spindle is the most essential process that takes place before and throughout the metaphase. The microtubules can bind to the kinetochore of each centromere. Fibers wander through the cytoplasm as they expand in this manner, 3 steps forward, 2 steps back. The unstable end of the fibers adds and subtracts components as it comes closer to the chromosome. The fibers are stable around the centrosomes, but they become less stable as they reach out toward the chromosomes. These microtubules form bigger fibers that extend from the centrosomes. The centriole divides during the start of eukaryotic cell division and starts forming the microtubule network that will transport chromosomes and organelles throughout the cell division process. The process of cell division is finished once the sister chromatids that make up the chromosomes have been separated after the stage of metaphase in the cell cycle. This moves them to the center of the cell. During the process of the microtubules retracting, an equal amount of tension is exerted on the chromosomes from both sides of the cell. Microtubules that originate on either side of the cell get attached to the respective chromosomes.
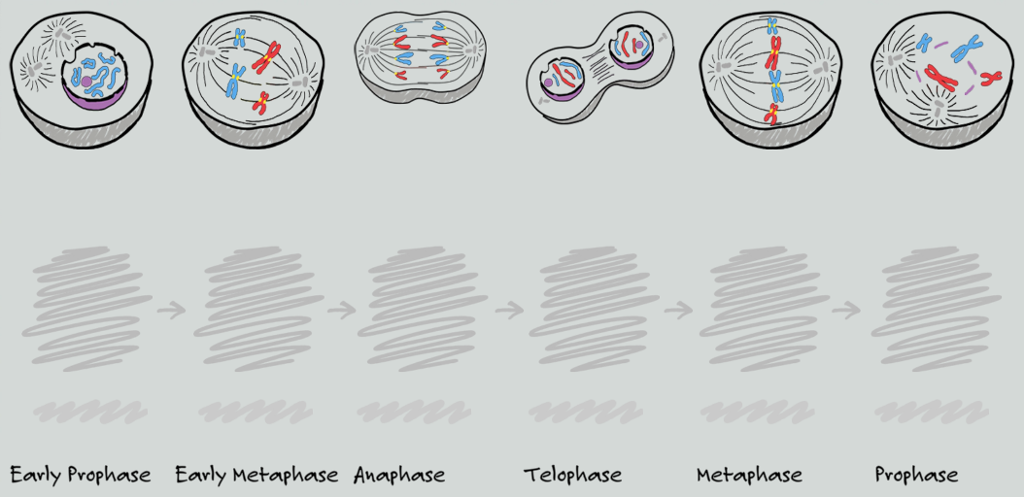
Prophase anaphase metaphase telophase series#
The cell goes through a series of checkpoints while it is in early metaphase and late prometaphase to confirm that the spindle has been produced. Chromosomes align in the dividing cell’s center.The chromosomes of a cell compress and migrate together.The chromosomes are condensed, the spindle fibers develop, and the nuclear envelope is broken down during these stages of cell division. Prophase and prometaphaseare the stages that precede metaphase. It is the second-most compacted and coiled stage of mitosis. The chromosomes align on the metaphase plate in the center of the cell during metaphase in eukaryotic cell division. During metaphase, a cell’s chromosomes, which carry genetic information, are aligned at the center (which will eventually split into two sets at anaphase). Mitosis is the process by which a parent cell’s replicated genetic material is separated into two identical daughter cells. Metaphase is the third phase of mitosis after prophase and before anaphase. Metaphase in cytogenetics and cancer studies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
